



Next: Bibliography
Up: book
Previous: Exercises
Contents
-

- Constant amplitude scaler
-
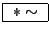
- Constant amplitude scaler
-
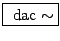
- Constant amplitude scaler
-
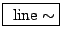
- Smoothed amplitude control with
-

- Conversion between frequency and
-
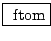
- Conversion between frequency and
-

- Conversion between frequency and
-

- Conversion between frequency and
-

- Conversion between frequency and
-

- Conversion between frequency and
-

- Wavetable oscillator
-

- Wavetable lookup in general
-

- Wavetable lookup in general
-

- Wavetable lookup in general
-

- Using a wavetable as
-

- Looping samplers
-

- Looping samplers
-

- Overlapping sample looper
-

- Overlapping sample looper
-
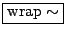
- Overlapping sample looper
-
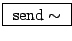
- Overlapping sample looper
-

- Overlapping sample looper
-
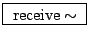
- Overlapping sample looper
-
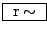
- Overlapping sample looper
-
 ,
,

- Control operations in Pd
-

- Control operations in Pd
-

- Control operations in Pd
-
 ,
,

- Control operations in Pd
-
- Converting controls to signals
-

- Converting controls to signals
-

- Signals to controls
-
- Signals to controls
-

- MIDI-style synthesizer
-

- MIDI-style synthesizer
-
 ,
,
- MIDI-style synthesizer
-

- Encapsulation in Pd
-

- Encapsulation in Pd
-

- Encapsulation in Pd
-

- Encapsulation in Pd
-

- Transfer functions for amplitude
-

- Additive synthesis: Risset's bell
-

- Additive synthesis: Risset's bell
-

- Polyphonic synthesis: sampler
-

- Polyphonic synthesis: sampler
-

- Polyphonic synthesis: sampler
-

- Polyphonic synthesis: sampler
-

- Octave divider and formant
-

- Waveshaping and difference tones
-
- The PAF generator
-

- Fixed, noninterpolating delay line
-

- Fixed, noninterpolating delay line
-

- Variable delay line
-
- Order of execution and
-
- Order of execution and
-
- Prefabricated low-, high-, and
-

- Prefabricated low-, high-, and
-
- Prefabricated low-, high-, and
-

- Prefabricated low-, high-, and
-
- Prefabricated time-varying band-pass filter
-

- Using elementary filters directly:
-

- Using elementary filters directly:
-

- Using elementary filters directly:
-
- Using elementary filters directly:
-

- Using elementary filters directly:
-

- Using elementary filters directly:
-

- Fourier analysis and resynthesis
-

- Fourier analysis and resynthesis
-

- Fourier analysis and resynthesis
-
- Fourier analysis and resynthesis
-

- Narrow-band companding: noise suppression
-

- Narrow-band companding: noise suppression
-

- Phase vocoder time bender
-

- Phase vocoder time bender
- absolute value (of a complex number)
- Complex numbers
- abstraction
- Encapsulation in Pd
- additive synthesis
- Periodic Signals
- examples
- Additive synthesis: Risset's bell
| Additive synthesis: spectral envelope
- ADSR envelope generator
- Envelope Generators
- aliasing
- The sampling theorem
- all-pass filter
- Power conservation and complex
- amplitude
- Sinusoids, amplitude and frequency
| Measures of Amplitude
- complex
- Complex sinusoids
- amplitude, measures of
- Measures of Amplitude
- amplitude, peak
- Measures of Amplitude
- amplitude, RMS
- Measures of Amplitude
- angle of rotation
- Power conservation and complex
- argument (of a complex number)
- Complex numbers
- arguments
- creation
- Quick Introduction to Pd
- audio signals, digital
- Sinusoids, amplitude and frequency
- band-pass filter
- Band-pass and stop-band filters
- bandwidth
- Designer spectra
| Band-pass and stop-band filters
- beating
- More additive synthesis
- Bessel functions
- Sinusoidal waveshaping: evenness and
- box
- Quick Introduction to Pd
- GUI
- Quick Introduction to Pd
- message
- Quick Introduction to Pd
- number
- Quick Introduction to Pd
- object
- Quick Introduction to Pd
- carrier frequency
- Frequency and phase modulation
| Carrier/modulator model
- carrier signal
- Multiplying audio signals
- center frequency
- Designer spectra
| Band-pass and stop-band filters
- Central Limit Theorem
- Waveshaping
- cents
- Frequency
- Chebychev polynomials
- Waveshaping using Chebychev polynomials
- class
- Quick Introduction to Pd
- classical waveforms
- Classical waveforms
- clipping
- Wavetables and samplers
- clipping function
- Waveshaping
- coloration
- Artificial reverberation
- comb filter
- Delay networks
- recirculating
- Recirculating delay networks
- compander
- Narrow-band companding
- complex conjugate
- Non-recirculating filter, second form
- complex numbers
- Complex numbers
- compound filter
- Compound filters
- continuous spectrum
- Taxonomy of spectra
- control
- Control
- control stream
- Control streams
- numeric
- Control streams
- covariance
- Superposing Signals
- creation arguments
- Quick Introduction to Pd
- DC
- Taxonomy of spectra
| One-pole, one-zero high-pass filter
- debouncing
- Event detection
- decibels
- Units of Amplitude
- delay
- compound
- Operations on control streams
- in Pd
- Control operations in Pd
- on control streams
- Operations on control streams
- simple
- Operations on control streams
- delay network
- linear
- Delay networks
- delay, audio
- Delay networks
- digital audio signals
- Sinusoids, amplitude and frequency
- Dirichlet kernel
- Fourier transform of DC
- discrete spectrum
- Taxonomy of spectra
- distortion
- Waveshaping
- Doppler effect
- Variable and fractional shifts
- duty cycle
- Timbre stretching
- dynamic
- Units of Amplitude
- dynamic range
- Narrow-band companding
- echo density
- Artificial reverberation
- elementary filter
- non-recirculating
- Elementary non-recirculating filter
- recirculating
- Elementary recirculating filter
- encapsulation
- Encapsulation in Pd
- envelope follower
- Event detection
| Envelope following
- envelope generator
- Synthesizing a sinusoid
| Envelope Generators
- ADSR
- Envelope Generators
- resetting
- Muting
- equalization
- Equalizing filters
- event
- Control streams
- event detection
- Event detection
- feedback
- Phase-aligned formant (PAF) generator
- filter
- Delay networks
| Filters
- all-pass
- Power conservation and complex
| All-pass filters
- band-pass
- Band-pass and stop-band filters
- Butterworth
- Butterworth filters
- compound
- Compound filters
- elementary non-recirculating
- Elementary non-recirculating filter
- elementary recirculating
- Elementary recirculating filter
- high-pass
- Low-pass and high-pass filters
- low-pass
- Low-pass and high-pass filters
- peaking
- Equalizing filters
- shelving
- Equalizing filters
- first difference
- Fourier series of the
- foldover
- The sampling theorem
- formant
- Designer spectra
- Fourier analysis
- Fourier analysis and resynthesis
- Fourier transform
- Fourier analysis of periodic
- fast (FFT)
- Fourier analysis and resynthesis
- phase shift formula
- Shifts and phase changes
- time shift formula
- Shifts and phase changes
- windowed
- Fourier analysis of non-periodic
- frequency
- carrier
- Frequency and phase modulation
- modulation
- Frequency and phase modulation
- frequency domain
- Delay networks
- frequency modulation
- More additive synthesis
| Frequency and phase modulation
- frequency response
- Delay networks
- frequency, angular
- Sinusoids, amplitude and frequency
- fundamental
- Periodic Signals
- gain
- Delay networks
- granular synthesis
- Sampling
- GUI box
- Quick Introduction to Pd
- half-step
- Frequency
- Hann window function
- Pulse trains via wavetable
- Hanning window function
- Pulse trains via wavetable
| Fourier analysis of non-periodic
- harmonic signal
- Taxonomy of spectra
- harmonics
- Periodic Signals
- high-pass filter
- Low-pass and high-pass filters
- hop size
- Fourier analysis and reconstruction
- imaginary part of a complex number
- Complex numbers
- impulse
- Delay networks
| Sawtooth wave
- impulse response
- Recirculating delay networks
- index
- of modulation
- Frequency and phase modulation
- waveshaping
- Waveshaping
| Waveshaping using Chebychev polynomials
- inharmonic signal
- Taxonomy of spectra
- interference
- Time shifts and delays
- intermodulation
- Waveshaping
- Karplus-Strong synthesis
- Order of execution and
- logical time
- Control
- low-pass filter
- Low-pass and high-pass filters
- magnitude (of a complex number)
- Complex numbers
- merging control streams
- Operations on control streams
- in Pd
- Control operations in Pd
- message box
- Quick Introduction to Pd
- messages
- Quick Introduction to Pd
| Control operations in Pd
- MIDI
- Frequency
- modulating signal
- Multiplying audio signals
- modulation
- frequency
- More additive synthesis
| Frequency and phase modulation
- ring
- Multiplying audio signals
- muting
- Muting
- noise gate
- Narrow-band companding
- noisy spectrum
- Taxonomy of spectra
- number box
- Quick Introduction to Pd
- numeric control stream
- in Pd
- Control operations in Pd
- Nyquist theorem
- The sampling theorem
- object box
- Quick Introduction to Pd
- octave
- Frequency
- oscillator
- Synthesizing a sinusoid
- parabolic wave
- Dissecting classical waveforms
- parent
- Encapsulation in Pd
- partials
- Taxonomy of spectra
- passband
- Low-pass and high-pass filters
- patch
- Synthesizing a sinusoid
| Quick Introduction to Pd
- peaking filter
- Equalizing filters
- period
- Periodic Signals
- phase locking
- Phase relationships between channels
- phase-aligned formant (PAF)
- Phase-aligned formant (PAF) generator
- Pitch/Frequency Conversion formulas
- Frequency
- polar form (of a complex number)
- Complex numbers
- pole-zero plot
- Designing filters
- polyphony
- Polyphony
- power
- Measures of Amplitude
- power series
- Waveshaping
- pruning control streams
- Operations on control streams
- in Pd
- Control operations in Pd
- quality (``q'')
- Impulse responses of recirculating
- real part of a complex number
- Complex numbers
- real time
- Control
- rectangle wave
- Classical waveforms
- rectangular form (of a complex number)
- Complex numbers
- reflection
- Power conservation and complex
- resynchronizing control streams
- Operations on control streams
- in Pd
- Control operations in Pd
- ring modulation
- Multiplying audio signals
- ripple
- Low-pass and high-pass filters
- sample number
- Sinusoids, amplitude and frequency
- sample rate
- Sinusoids, amplitude and frequency
- sampling
- Sampling
- examples
- Polyphonic synthesis: sampler
- sawtooth wave
- Wavetables and samplers
| Classical waveforms
- settling time
- Impulse responses of recirculating
- shelving filter
- Equalizing filters
- sidebands
- Multiplying audio signals
- sidelobes
- Resulting spectra
| Fourier transform of DC
- signals, digital audio
- Sinusoids, amplitude and frequency
- spectral envelope
- Sampling
| Taxonomy of spectra
- spectrum
- Taxonomy of spectra
- square wave
- Sawtooth waves and symmetry
- stable delay network
- Recirculating delay networks
- stopband
- Low-pass and high-pass filters
- stopband attenuation
- Low-pass and high-pass filters
- subpatch
- Encapsulation in Pd
- subpatches
- Encapsulation in Pd
- subtractive synthesis
- Subtractive synthesis
| Predicting and controlling foldover
- switch-and-ramp technique
- Switch-and-ramp
- tags
- Voice tags
- tasks
- Voice allocation
- threshold detection
- Event detection
- timbre stamping
- Timbre stamping (classical vocoder)
- timbre stretching
- Timbre stretching
| Carrier/modulator model
- time domain
- Delay networks
- time invariance
- Time shifts and phase
- time sequence
- Control streams
- toggle switch
- More additive synthesis
- transfer function
- Linear and Curved Amplitude
| Waveshaping
| Filters
- transient generator
- Envelope Generators
- transition band
- Low-pass and high-pass filters
- triangle wave
- Classical waveforms
- unit generators
- Synthesizing a sinusoid
- unitary delay network
- Power conservation and complex
- vocoder
- Timbre stamping (classical vocoder)
- voice bank
- Polyphony
- von Hann window function
- Fourier analysis of non-periodic
- wave packet
- Resulting spectra
- waveshaping
- Waveshaping
- wavetable lookup
- Wavetables and samplers
- non-interpolating
- Wavetables and samplers
- wavetables
- transposition formula for looping
- Sampling
- transposition formula, momentary
- Sampling
- window
- Measures of Amplitude
| Fourier analysis and reconstruction
- window function
- Fourier analysis of non-periodic
- window size
- Pitch shifting
Miller Puckette
2006-12-30